1.Measuring Population Health
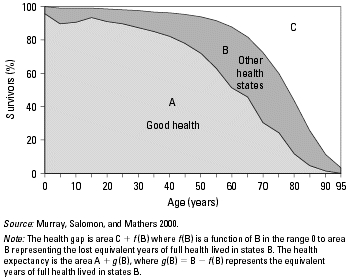
- Health Expectancy Measure
- Health Gap Measure
- Value of a Statistical Life
- Value of a Statistical Life Years
2. Risk Factor Analysis
2.1 Individual vs Population
- Individual Approach
- Advantage
- Appropriate for individual
- Subject motivation
- Physician motivation
- Cost-effective
- Favorable to benefit
- Drawback
- Difficulties and costs of screening
- Palliative and temporary
- Limited
- Large number of people at a small risk ay give rise to more case than the small number of people who are at high risk
- Behaviorally inappropriate-it’s hard for a person to do things differently from everyone else around him
- Population Approach
- Advantage
- Radical
- Large Potential for Population
- Behaviorally appropriate
- Drawbacks
- Small benefit to each individual
- Poor motivation of physician as they see only small changes in patients for all the efforts they put in
- Benefit: risk ratio worrisome
- Example: Japan: Metabolic Syndrome
2.2.Determinant of Health
Prevalence and relative risk of risk factors explain
imageプラグインエラー : 画像を取得できませんでした。しばらく時間を置いてから再度お試しください。
2.3.Transitions
- Demographic Transition
- Epidemiologic Transition
- Exception
- Former USSR
- Sub-Saharan Africa
- Health Transition?
- Based on Julio Frenk's idea of health transition, Vallin and Melse introduced three transition process in terms of divergence/convergence sequences by successful changes in health technologies and strategies.
- Three Process of Health Transition
- Epidemiologic transition as first stage of health transition
- Intruduced in developed countries first, then diffused into developing countries
- Cardiovascular Revolution
- Started in developing countries in the mid-60s, but not diffused into developing countries
- Slowing the Aging Process
- Introduction and Key
- Ezzati M et. al.(1)
- Powles(2)
- Murray CJL et. al(3)
- Vander Hoorn S et. al.(4)
- Risk factor exposure
- Exposure quantification and exposure variable
- Population exposure distributions and counter-factual exposure distribution
- Exposure data sources and exposure models
- Fishman et. al.: Childhood and maternal underweight
- Bull et. al.: Physical activity vs physical fitness
- Risk factor hazardous effects
- Quantification of hazardous effect: heterogeneity and extrapolation(Yusuf et. al.)
- Hazard accumulation
- Multiple risk factors and multi-risk quantification
- Multi-risk models and multi-risk quantification
- Mediated hazard and effect modification
- Risk factor correlation and risk factor-disease correlation
- Murray et. al.: Eight distinct population subgroups in the US
- Temporal Dimension and Application
[Links]
最終更新:2011年01月25日 19:47